

Strolling through a serene forest, surrounded by trees that hold secrets of centuries. Among these giants, the cork oak stands tall, offering a glimpse into a world where nature and sustainability intertwine. This captivating journey into the realm of cork is not just a tale of a material; it’s a testament to eco-friendly practices that resonate deeply with our planet’s health.
Is cork sustainable? Let’s embark on this exploration to uncover its unique properties, environmental benefits, and the role it plays in supporting local economies. Get ready to delve into the world of cork and its sustainable charm.
Cork is a fascinating material that comes from the bark of cork oak trees, mainly found in the Mediterranean region. Its sustainable harvesting process ensures that the trees are preserved and continue to thrive.
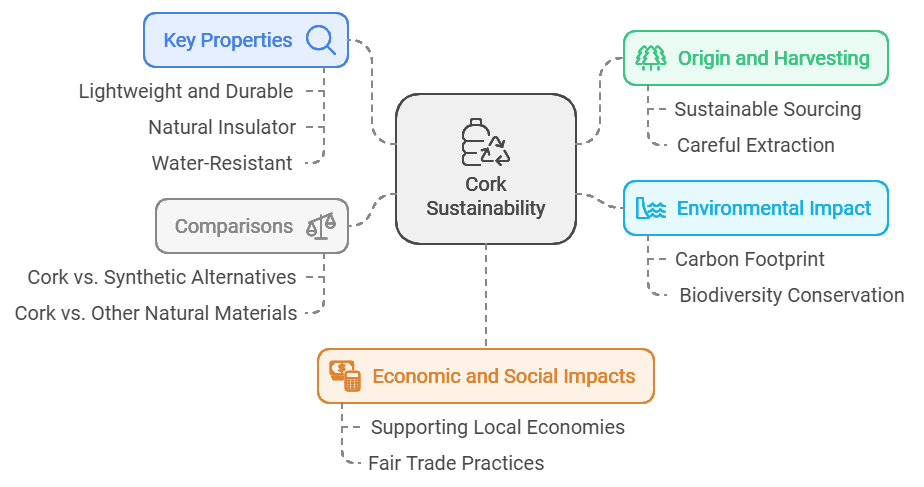
Cork is celebrated for its ecological benefits and its wide range of uses, making it a popular choice in many industries. Let’s explore how cork is sourced and the unique properties that make it so versatile.
Also Read: Carbon Footprint Reduction: 10+ Life-Changing Tips
Cork production is a shining example of how nature and industry can work hand in hand. It offers an environmentally friendly alternative while promoting ecological balance.

By exploring its carbon footprint and biodiversity conservation efforts, we can understand why cork is a preferred choice for sustainability enthusiasts.
Cork production is notably gentle on our planet, boasting several environmental benefits:
Cork forests play a pivotal role in preserving biodiversity:
When considering materials, cork often comes into the spotlight due to its unique characteristics. It’s fascinating to explore how cork measures up against synthetic alternatives and other natural materials.
These comparisons help us understand the benefits and limitations of each, aiding in making informed choices.
| Factor | Cork | Synthetic Alternatives |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Renewable resource; harvested without damaging trees, allowing continuous carbon absorption. | Made from non-renewable fossil fuels; not biodegradable, contributing to pollution. |
| Functionality | Naturally compresses and expands, creating a secure seal with slight oxygen transfer, aiding wine aging. | Provides a consistent seal but lacks oxygen exchange, which may affect wine maturation; can become too tight over time. |
| Quality Control | Risk of cork taint, but improved quality control reduces contamination risks. | Eliminates cork taint risk but may add a chemical taste if not manufactured correctly. |
| Aspect | Cork | Other Natural Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainability | Cork forests support biodiversity, and sustainable harvesting practices maintain these ecosystems. | Bamboo or eucalyptus may lack similar ecological benefits if harvested unsustainably. |
| Usability | Cork offers flexibility and resilience, making it suitable for applications beyond bottle closures, such as insulation and flooring. | Materials like wood or bamboo are often more rigid and limited in applications compared to cork. |
| Durability | Cork is highly durable, resistant to moisture and temperature changes, helping products maintain quality over time. | Wood may degrade more easily and often requires greater maintenance. |
Cork production plays a vital role in shaping economic and social elements, particularly in areas where cork oak forests are abundant. Let’s explore how this industry aids local economies and promotes fair trade practices, ensuring a sustainable future for communities involved.

In places like Portugal, cork production is more than just an industry; it’s a way of life. It provides much-needed employment opportunities to countless families, helping to sustain the local economy. What’s fascinating is how it intertwines with cultural heritage as communities use traditional methods to harvest cork sustainably.
This process not only keeps the environment healthy but also ensures that the local economy thrives. By maintaining a balance between modern techniques and age-old wisdom, cork production supports small businesses and helps preserve cultural traditions.
The cork industry is making strides in embracing fair trade practices, ensuring that workers receive fair wages and work in safe environments. These practices are crucial in promoting ethical labor standards, helping to uplift the communities involved.
By choosing products that adhere to fair trade principles, consumers can support equitable resource distribution and the welfare of workers. This approach not only enhances the industry’s image but also encourages environmentally and socially responsible consumption.
Also Read: Sustainable Diet Essentials: Your Complete Guide
Cork sustainability is set to evolve dramatically with the integration of new practices and technologies. Future trends are pointing towards a greater emphasis on biodegradable cork products, as well as the use of plant-based materials in production. This shift aims to decrease dependence on synthetic alternatives.
Additionally, many companies are prioritizing carbon-neutral processes, which amplify the environmental benefits of cork harvesting. Importantly, cork harvesting is gentle on trees, allowing them to continue absorbing carbon dioxide.
The increasing demand for eco-friendly packaging is also boosting cork’s popularity, cementing its importance in sustainable growth and environmental conservation.
Cork stands as a testament to sustainable practices in material production. With its low carbon footprint and support for biodiversity, cork not only serves as a functional material but also upholds environmental values. Its ability to support local economies and encourage fair trade practices further solidifies its importance.
As we delve into the future, innovations in cork sustainability are likely to enhance its role even more. Thus, embracing cork is a step toward a more sustainable world. To discover more about eco-friendly materials and their impacts, explore our other insightful articles. Keep reading to stay informed and inspired!
